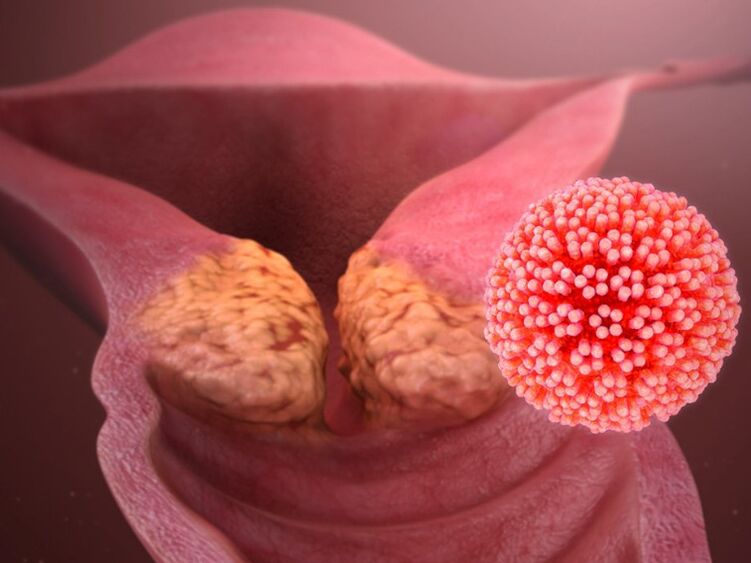
Human papillomavirus (HPV) provokes the formation of papillomas, warts, condyloma and is a triggering factor in the development of cancer of the cervix and larynx. Less commonly, it can affect the oral mucosa, esophagus, conjunctiva of the eyes. WorldAccording to the health organization, cases of this infection have increased 10 times in the last 10 years. In our country, the prevalence of HPV infection, according to studies across regions, varies from 29% to 45%. The medical community is particularly concerned due to this fact. Beware that about a third of all isolated virus genotypes provoke the development of oncological pathology.
Classification of the course of papillomavirus infection
Entering a woman's body, HPV can show different activity, depending on the state of immunity. Depending on how the pathogen behaves, there are several types of human papillomavirus infection:
- latent flow. The virus persists in the body, but does not cause pathological changes in cells. There are no symptoms - the presence of a microorganism can only be determined using molecular biological research methods.
- Inflammation associated with HPV. As a rule, we are talking about cervicitis or vulvovaginitis on the background of HPV, which leads the patient to a gynecologist. By consultation, she can find out: HPV in womenHow to treat. It should be understood that the virus itself does not cause inflammation, but creates conditions for the activation of the inflammatory process.
- Condyloma located in the genital area and on the mucous membrane of the genital tract is a form of the course of PVI (papillomavirus infection), in which it becomes necessary to use modern surgical techniques to remove the formations. Surgical removal, laser destruction, cryodestruction or radioAfter wave coagulation, complex treatment is required to prevent complications and recurrence.
- Cervical dysplasia. May be asymptomatic or cause discharge. Severe forms of the disease are pre-cancerous - to avoid this condition, more accurate understanding of how HPV is treated in women than ever beforeis more important.
Classification helps the doctor choose the most effective treatment strategy. Pathogen strains are divided into groups depending on their ability to cause oncological diseases: HPV with high, medium and low oncogenic risk. Of the 40 types, 14 are classified as high and moderate oncogenic risk: -16, -18, -31, -33, -35, -39, -45, -51, -52, -56, -58, -59, -66 and -68 types.
How is the human papillomavirus spread?
In the female population, HPV infection reaches up to 70%. However, the presence of a pathogen in the body does not necessarily mean a disease. If a person has a healthy immune system, HPV infection is, in most cases, transient in nature. Occurs - it disappears on its own within 2 years. If this does not happen, then the question becomes relevant how to treat human papillomavirus in women.
The main route of transmission of the virus is contact:
- sexual;
- vertical (from mother to fetus during childbirth);
- household (when using a towel, razor, underwear).
Young people aged 13-30 are most susceptible to infection with this virus. At first sexual contact, the risk of infection is about 60%. The virus can enter the body even in the absence of direct sexual intercourse. Girls are most susceptible to HPV. There is a greater danger, and then with its consequences. This is due to the peculiarities of the structure of their genital organs.
Human papillomavirus in women: causes
In the female population, HPV infection reaches up to 70%. However, the presence of a pathogen in the body does not necessarily mean a disease. If a person has a healthy immune system, HPV infection is, in most cases, transient in nature. Occurs - it disappears on its own within 2 years. If this does not happen, then the question becomes relevant how to treat human papillomavirus in women.
- concomitant pathologies of the reproductive system;
- endocrine disorders;
- immunodeficiency and beriberi;
- frequent acute infectious diseases - SARS, other viral and bacterial infections;
- early intercourse;
- abortion;
- Smokin Drink;
- chronic psycho-emotional stresses that weaken the immune system;
- excessive physical and emotional stress, irregular daily routine;
- postpartum period - due to stress and hormonal changes;
- Long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs and oral contraceptives.
Frequent change of sexual partners increases the risk of both infection with new strains of the virus and activation of existing infections. If immunity is reduced, the virus integrates into the cellular genome, which has a high potential for cancer. How to treat HPV in women at this stage of medical science is yet to be discovered. Therefore, it is very important to keep the activity of the virus under control and to stimulate the immune defense properly.
First signs and additional symptoms of HPV in women
The most obvious sign of the presence of HPV in a woman's body is the appearance of papillomas on the mucous membranes of the genital organs and the skin of the anogenital region. They do not cause pain and, as a rule, remain unnoticed for a long timeHowever, the activity of the virus can provoke the appearance of other unpleasant symptoms, because of which a woman will immediately contact a gynecologist:
- pathological discharge from the vagina, accompanied by itching and burning;
- frequent relapses of vaginitis, bacterial vaginosis;
- foul-smelling vaginal discharge.
On examination, the doctor sees benign formations on the skin, changes in the epithelium of the cervix, signs of inflammation. Cancer can appear only in the later stages of chronic papillomavirus infection.
Is there a cure for human papillomavirus?
To understand how HPV is currently being treated in women, it is necessary to understand what approaches exist in the treatment of human papillomavirus infection. At the moment, HPV infection therapy has been limited to the following activities:
- prevention of progression of HPV infection;
- elimination of clinical manifestations;
- Stimulation of systemic and local antiviral immunity.
There is no drug that can completely make the virus disappear from the body. However, research in this area continues - the attention of doctors is focused on the need for combined treatment of various manifestations of HPV. Research in the field of genetic engineering is promising. Scientists are looking at the possibility of "rewriting" the viral code to destroy itself rather than spreading it. Reducing the viral copies restores local immunity and eliminates chronic inflammation.
Information for doctors on the topic "How to treat HPV in women" is detailed in the current clinical guidelines.
When is it necessary to see a doctor?
Women should undergo a preventive examination by a gynecologist at least once a year. In addition, there is a need to visit a doctor if any troubling symptoms appear:
- neoplasms in the genital area;
- warts on other areas of the skin and mucous membranes;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- unusual discharge or bad odor from the vagina;
- Itching, swelling, redness of the genitals.
In a situation where accidental intercourse has occurred, it is advisable to visit a gynecologist. He will conduct an examination, do gynecological smears and scrapings to detect HPV.
If papillomas occur in other parts of the body, consultation with a dermatologist is necessary. When papillomas or condylomas grow in the anus, the intervention of a proctologist may be required. This will help determine the treatment strategy and anyWhat remedies for papillomas should be prescribed to the patient for purchase in a pharmacy in a particular case.
general plan of therapy
The primary weapon in the fight against HPV is the stable immunity of the individual itself. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention draws attention to the fact that 90% of cases of exposure to the virus are clinically due to self-suppression of the virus by natural immunity. Expressions do not develop.
Treatment for HPV infection should be comprehensive and objective:
- therapy of concomitant diseases;
- Elimination of external manifestations of diseases - medically and, if necessary, surgically;
- decrease in viral load;
- Stimulation of the body's own defenses.
Chronic psycho-emotional stress, poor environment and co-morbidities impair a woman's immune system's ability to deal with viruses on its own. There are drugs that have direct antiviral and immunomodulatory effects, helping the body strengthenand reduce viral load. These modern drugs include a spray with active glycyrrhizic acid, which is derived from licorice root. This helps prevent the virus from replicating too quickly and prevents copies of the HPV genetic material in the body. Reduces the number. The tool has a special intravaginal nozzle for drug delivery to the cervix and uniform distribution along the walls of the vagina. Antiviral and immunomodulatory therapy in the latent course of papillomavirus infection in the presence of unpleasant symptoms and in more aggressive forms of infectionCan prevent infection. If the virus provoked changes in the epithelium of the genital area and cervix, the spray helps:
- relief from inflammation;
- eliminate itching;
- restore the integrity of the mucosa;
- Enhancement of local immunity.
The use of the product is also indicated in the preparatory period to remove benign formations caused by HPV, reduce virus activity and prevent relapse. The drug can regenerate the skin and prevent the attachment of secondary infections. helps in
Removal of papillomas and warts
Benign formations caused by HPV are subject to removal, which can be performed by the following methods:
- cryodestruction - exposure of the neoplasm with freezing;
- electrocoagulation - treatment with high-frequency current;
- laser removal - layer-by-layer exposure to laser radiation until a crust appears;
- chemical destruction - treatment with special chemical solutions that are applied to warts and destroy them;
- Surgical removal - given the high risk of recurrence after this type of destruction, it is prescribed selectively - if it is impossible to use other methods.
Among the new developments in the treatment of HPV is the CRISPR/Cas9 system, which almost completely cleaves DNA and embeds sections of it, thereby inactivating further spread of the virus.
Redressal
For primary prevention, it is recommended to use barrier contraception (condom), which although not complete protection against HPV, will reduce the level of exposure to the virus. You have to be selective in choosing your sexual partner of choice. Should an accidental connection occur, a special spray may be used to protect against HPV, herpes simplex virus and cytomegalovirus infection.
To date, HPV vaccination is the most effective. It protects against the most common and deadly types of human papillomavirus. In many countries, HPV vaccination is included in the mandatory vaccination calendar. The most effective times for vaccination are in childhood and adolescence. It used to be thought to make no sense 20 years after vaccination. But recent studies have shown that HPV vaccination is appropriate and effective up to the age of 45-47.
If there is a virus infection, the task of secondary prevention is to maintain the good health of the patient, especially the good state of his immune system. Women should have regular gynecology to detect virus-associated diseases at an early stage. Must go to specialist.














































































